在 ASP.NET Core 中实现缓存:提升应用性能的实用指南
缓存是一种极其高效的性能优化手段,它通过将数据临时存储在更快的访问位置,从而避免频繁的昂贵计算或数据库查询。ASP.NET Core 提供了多种缓存机制,方便我们在不同业务场景中灵活选择。
缓存如何提升性能
缓存的核心价值在于减少延迟、降低服务器负载,并提升用户体验。在一次实际项目中,仅通过引入 Redis 分布式缓存,我们就成功支撑了超过 100 万用户的访问量,而后台只运行了一台 SQL Server 主库和一个只读副本。缓存的威力可见一斑。
ASP.NET Core 缓存抽象
ASP.NET Core 提供了两大核心缓存接口:
IMemoryCache:进程内缓存,速度快但受限于单实例内存。IDistributedCache:分布式缓存接口,可接入 Redis、SQL Server 等后端存储。
注册方式非常简单:
builder.Services.AddMemoryCache();
builder.Services.AddDistributedMemoryCache();以 IMemoryCache 为例,实现方式是先检查缓存中是否存在数据,如果不存在再从数据库获取并写入缓存:
app.MapGet("products/{id}", (int id, IMemoryCache cache, AppDbContext context) =>
{
if (!cache.TryGetValue(id, out Product product))
{
product = context.Products.Find(id);
var options = new MemoryCacheEntryOptions()
.SetAbsoluteExpiration(TimeSpan.FromMinutes(10))
.SetSlidingExpiration(TimeSpan.FromMinutes(2));
cache.Set(id, product, options);
}
return Results.Ok(product);
});通过 AbsoluteExpiration 与 SlidingExpiration 我们可以精细控制缓存的有效期,防止数据陈旧。
Cache-Aside 模式
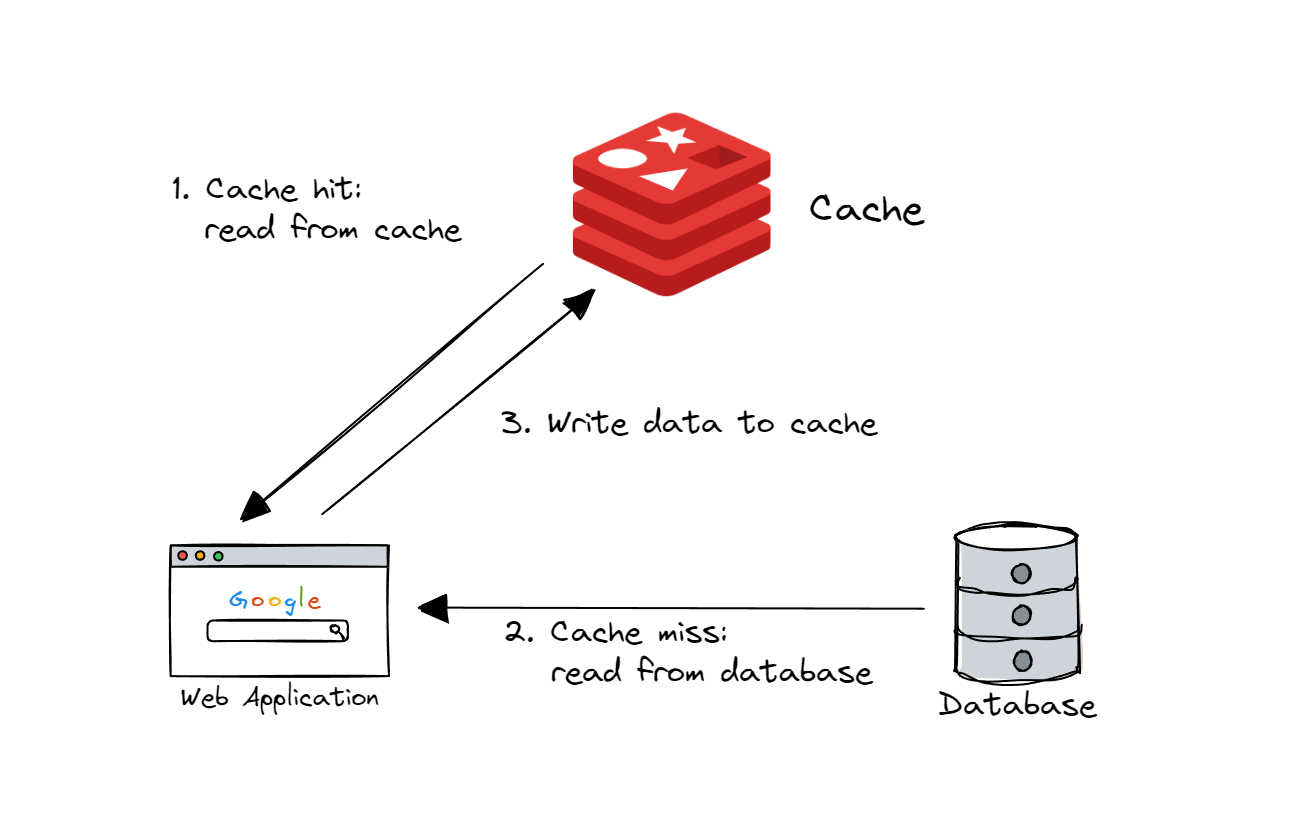
Cache-Aside(旁路缓存)是最常用的策略:先查缓存,未命中则查数据库并回填缓存。在分布式场景中,我们可以为 IDistributedCache 编写扩展方法,简化重复逻辑:
public static async Task<T> GetOrCreateAsync<T>(
this IDistributedCache cache, string key, Func<Task<T>> factory,
DistributedCacheEntryOptions? options = null)
{
var cached = await cache.GetStringAsync(key);
if (cached is not null)
return JsonSerializer.Deserialize<T>(cached);
var data = await factory();
await cache.SetStringAsync(key, JsonSerializer.Serialize(data),
options ?? new DistributedCacheEntryOptions
{
AbsoluteExpirationRelativeToNow = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(2)
});
return data;
}调用时只需一行:
var product = await cache.GetOrCreateAsync($"products-{id}",
() => context.Products.FindAsync(id));分布式缓存与 Redis 集成
在生产环境中,Redis 是最常用的分布式缓存。通过 Microsoft.Extensions.Caching.StackExchangeRedis 包,可以无缝将 IDistributedCache 接口绑定到 Redis。
builder.Services.AddStackExchangeRedisCache(options =>
{
options.Configuration = builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("Redis");
});或者使用 IConnectionMultiplexer 提升连接管理能力:
var mux = ConnectionMultiplexer.Connect(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("Redis"));
builder.Services.AddSingleton(mux);
builder.Services.AddStackExchangeRedisCache(options =>
{
options.ConnectionMultiplexerFactory = () => Task.FromResult(mux);
});缓存雪崩与并发控制
缓存雪崩(Cache Stampede)是在高并发下多请求同时未命中缓存、直击数据库的现象。ASP.NET Core 中可以利用 SemaphoreSlim 为同一 Key 加锁,避免重复查询。
private static readonly SemaphoreSlim Semaphore = new(1, 1);
await Semaphore.WaitAsync();
try
{
// 双重检查后填充缓存
}
finally
{
Semaphore.Release();
}这种方式可进一步优化为“按 Key 粒度加锁”,减少全局锁竞争。
.NET 9 的 HybridCache
.NET 9 引入的 HybridCache 结合了内存缓存与分布式缓存的优点,旨在降低 IDistributedCache 的序列化开销并减少缓存击穿风险。它在本地维护一份副本,从而在分布式系统中依然能提供接近内存级的读取速度。
总结
ASP.NET Core 的缓存体系为性能优化提供了强大支持:
IMemoryCache 适合单机、低延迟场景;
IDistributedCache 与 Redis 则面向高可用、可扩展架构;
.NET 9 的 HybridCache 则可能成为未来的首选方案。
合理选择缓存策略、控制失效时间、处理并发场景,才能让缓存真正为系统稳定性与性能加分。
